BY  GENN
GENN
2024/06
Blog
Your Guide to Abrasion-Resistant Steel
This article introduces abrasion resistant steel plates and their types, main features, processes, uses, etc. It provides a wide range of benefits of wear resistant steel plates, including mining, recycling, energy, and cement. This article also discusses different types of wear resistant steel plates, such as AR400, AR450, AR500 wear plates. It introduces the main features and benefits of wear resistant steel plates, such as high hardness, excellent wear resistance, enhanced corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
WHAT IS ABRASION RESISTANT STEEL PLATE?
Abrasion Resistant (AR) steel plate is a high carbon alloy steel plate. This means that AR is harder due to the addition of carbon, and formable and weather resistant due to the addition of alloys.

The carbon added during the steel plate forming process greatly increases toughness and hardness, but reduces strength. Therefore, AR plate is used in applications where wear and abrasion are the primary causes of failure, such as industrial manufacturing, mining, construction, and material handling. AR plate is not suitable for structural construction uses such as support beams in bridges or buildings.
Kinds of Wear-Resistant Steel Plates:
Abrasion resistant plates are readily available in a number of kinds, each customized to satisfy particular sector requirements and applications. These plates are classified based on their make-up, hardness, and the procedures used to enhance their wear resistance. The main kinds consist of AR400, AR450, and AR500, which are usually named after their firmness rankings gauged on the Brinell range.
AR400:
The AR400 steel plate is a typical choice in applications where a good equilibrium between firmness and ductility is called for. With a solidity of roughly 400 HBW, AR400 plates are utilized in moderate wear environments. They use a great combination of impact resistance and toughness, making them appropriate for building equipment, commercial devices, and mining procedures.
AR450:
AR450 steel plates are developed for somewhat greater wear resistance compared to AR400. With a solidity of regarding 450 HBW, these plates offer enhanced sturdiness in much more unpleasant conditions. AR450 is commonly utilized in dump truck linings, mining devices, and product handling systems. The increased hardness aids in prolonging the life span of parts subjected to constant friction and influence.
AR500:
AR500 steel plates are known for their extraordinary hardness of about 500 HBW, making them perfect for high-wear settings. These plates are highly resistant to abrasion and are typically utilized in applications such as durable earthmoving, demolition devices, and ballistic protection. The premium hardness of AR500 lead to prolonged wear life, lowering the requirement for constant substitutes and upkeep.
Abrasion Resistant Steel Sheet Hardness Range And Thikness:
| Grade | Product | Thickness | Hardness Range |
| 500 AR | Cut Lengths | 4.0 – 5.5 | 450 – 540 |
| 500 AR | Heavy Plates | 5 – 60 | 450 – 540 |
| 400 AR | Cut Lengths | 2.5 – 6.4 | 360 – 420 |
| 400 AR | Heavy Plates | 5 – 15 | 360 – 420 |
| 400 AR | Heavy Plates | 15 – 30 | 360 – 450 |
| 400 AR | Heavy Plates | 30 – 60 | 360 – 480 |
| 450 AR | Cut Lengths | 3.0 – 6.4 | 420 – 500 |
| 450 AR | Heavy Plates | 6 – 60 | 420 – 500 |
| Type | Grades Desig- nation |
Chemical Composition (%)*1 | ||||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Mo | B | PCM (t:thickness)*2 | |||
| ≤t25 | t>25 | |||||||||||
| Standard Type | ABREX 400 |
≤0.21 | ≤0.70 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.025 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.20 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.35 |
| ABREX 450 |
≤0.23 | ≤0.70 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.025 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.20 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.36 | ≤0.36 | |
| ABREX 500 |
≤0.35 | ≤0.70 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.015 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.20 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.42 | ≤0.42 | |
| ABREX 600 |
≤0.45 | ≤0.70 | ≤2.00 | ≤0.015 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.20 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.60 | ≤0.005 | ≤0.54 | ||
Chemical Properties Of Abrasion Resistant Wear Plates:
Mechanical Properties Of Abrasion Resistant Steel Sheet:
| Type | Grades Desig- nation |
Thick-ness (mm) | Brinell Hardness (HBW) | Mechanical Properties | ||||||
| Yield Strength (N/mm2) | Tensile Strength (N/mm2) | Bend Radius (t:thickn-ess) | Angle | Result | Tempera-ture () | Absored Energy (j) | ||||
| Standard Type | ABREX 400 |
25 | 414, 417, 416 | 1075 | 1322 | 3t | No Cracking | 0 | 73 | |
| ABREX 450 |
25 | 458, 453, 459 | 1192 | 1469 | 3t | No Cracking | 0 | 57 | ||
| ABREX 500 |
25 | 513, 509, 520 | 1373 | 1552 | 3t | No Cracking | 0 | 43 | ||
| ABREX 600 |
25 | 611, 606, 601 | 1568 | 2058 | – | – | – | 0 | 13 | |
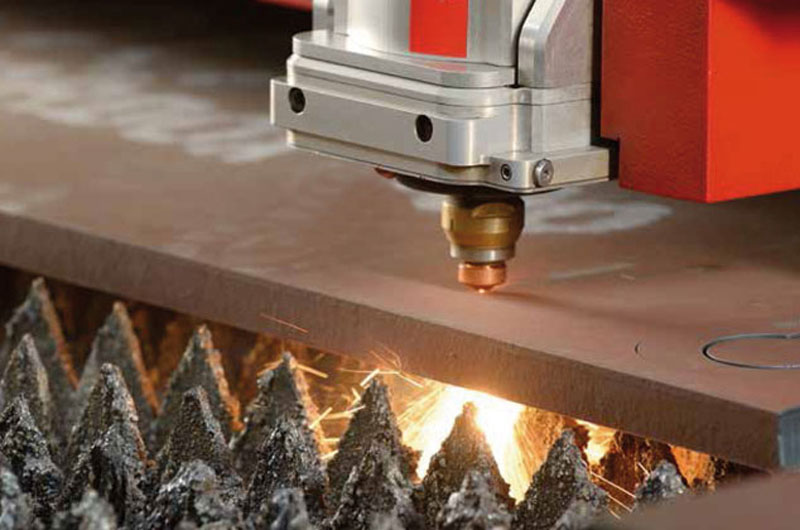
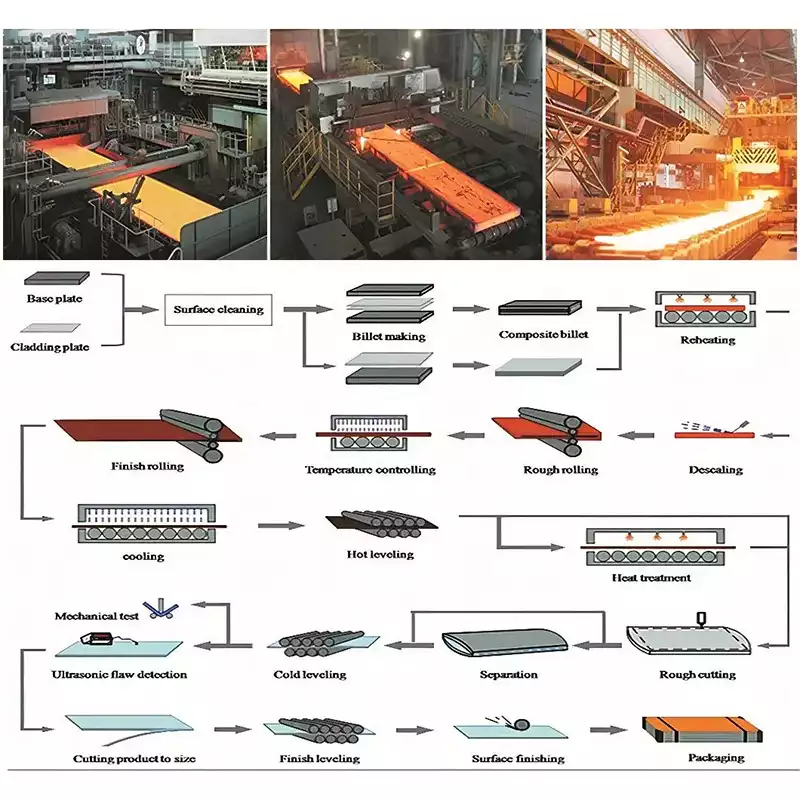
What Is the Process of Making Abrasion Resistant Metal?
- Quenching is the technique of rapidly chilling a substance or workpiece in water.
- Tempering,The procedure of heating the material to a higher temperature in the air is then used to treat it.
- The formation of crystal structures in the material occurs when a piece is heated and quenched, and this is what improves the metal’s hardness.
- Reheating it fractures the structures, as well as the crystals formed, which is responsible for the material’s malleability.
- It’s the repetition that makes it difficult, harsh, and more difficult to break.
Advantages of AR Steel :
The most common reason that industries and individuals use AR steel is for its durability, which makes it ideal for long-term use and continued wear. Some other great benefits of using AR steel include:

Long life and cost savings. Because AR steel has nearly unmatched durability, it ensures that your parts and machinery will last longer than standard steel parts. This means less replacement and maintenance, leading to greater savings in the long run.
Structural integrity. The combination of wear and impact resistance ensures the structural integrity of equipment and components. This makes AR steel valuable in heavy-duty applications where maintaining structural stability is critical.
Wear resistance. Obviously, wear resistance is a key benefit of using AR steel. The wear resistance provided by AR steel extends the life of your parts, allowing you to use them in almost any harsh environment without having to worry about them wearing out.
Uses of Abrasion-Resistant Steel:
Wear-resistant steels have a place in hundreds of industries and applications, but some uses are better suited than others. Ideally, AR steels are used in applications where there is constant motion and/or flow of abrasive materials. This allows parts and machinery to take full advantage of the impact and wear resistance that AR steels offer.
These applications are often found in:
- Construction equipment. Construction equipment, including structural beams, bulldozers, compactors, and more, can benefit from the use of AR steels, as most of this equipment comes in contact with highly abrasive media.
- Mining equipment. All tools used in mining and excavation need to be resistant to wear, abrasion, and impact. Heavy and highly abrasive materials often come in contact with tools, parts, and machinery used in this industry, making AR steel not only beneficial, but essential.
- Agricultural tools. The most common tools and equipment in the agricultural industry are lined with or made from wear-resistant steels. With constant outdoor use, these pieces of equipment directly benefit from the wear resistance that AR steels offer.
What Factors will Affect the Quality of Wear-Resistant Steel Plates?
Factor 1: Heat Treatment and Alloy Content
The hardness of wear-resistant steel plates is well defined. There are two main ways to improve the hardness and toughness of wear-resistant plates:
i. Heat Treatment (QT)
For certain specific working environments, such as earthworks and mining, quenching and tempering the steel through heat treatment processes is an economical option. However, these types of wear-resistant plates, while cost-effective, are not as durable as alloy wear-resistant plates.
ii. Adding Alloy Content
For alloy wear-resistant plates, there are 3 basic alloying elements: carbon, silicon, manganese, of course, other alloying elements can also improve different mechanical properties of wear-resistant steel plates:
Carbon: Increasing the carbon content in steel increases its yield point and tensile strength, but reduces its ductility and impact resistance. At the same time, too high a carbon content reduces the weldability of the steel, so adjusting the carbon content balance in the wear-resistant plate is a very important and non-negligible operation.
Silicon: Silicon can significantly increase the elastic limit, yield point and tensile strength of steel, but like carbon, too much silicon addition will also reduce the weldability of steel.
Manganese: Manganese is a good deoxidizer, desulfurizing during the steelmaking process, giving the wear-resistant plate higher strength and hardness, and also improving the hardenability and hot working properties of the steel.
Factor 2: Surface smoothness
When considering the service life of wear-resistant steel plates, especially in applications such as truck bodies, conveyor belts and fan blades, surface smoothness is a very critical factor. Smooth surfaces ensure uniform wear as well as bending radius, providing precise bending accuracy.
Factor 3: Hardness variation inside the steel plate
The core hardness value affects the service life of the wear part. For example, when wear occurs and new material is exposed, if the core hardness value of the steel plate is high, the wear rate will be minimized and the service life of the component will be extended compared to the steel plate with a lower core hardness value.