BY  GENN
GENN
2024/06
Blog
Ar400 Steel – Unmatched Through Hardness
This article introduces the advantages, typical properties, cutting methods, etc. of AR400 wear-resistant steel plate. It introduces the formability and weldability of AR400 wear-resistant steel plate. This article also discusses the difference between AR400 and AR500 wear-resistant plates. It introduces the hardness, cracking, application, cutting performance, weldability, etc. of AR400 and AR500 wear-resistant plates.
What Is AR400 Steel?
AR400 wear plates are one such plate that has high wear and abrasion resistance. They are commonly used in truck beds and attachments for bulldozers and excavators. The main property of these AR400 wear resistant steel plates is their hardness. Compared to mild steel, 400 series steel plates are 3 times harder. They are used in conveyors, buckets, construction machinery, excavators, and bulldozers. Therefore, AR400 wear plates are used in applications where wear resistance is crucial.
The benefit of using AR 400 wear resistant plates is that it significantly extends the life of the product. It also improves the durability, reliability, and safety of the product. AR 400 abrasion resistant steel plates are quenched for increased wear resistance and can be tempered for increased hardness. On the other hand, low salt water hardness plates have good cold bending and weldability. AR400 materials do not have a defined chemical property and are actually classified into two categories based on hardness. They can also be used in applications with impact or sliding wear.
Benefits of AR400 Wear Steel Plate
When determining which wear resistant steel is best for your application, it is important to note that each grade reacts differently to many manufacturing processes. AR400 abrasion resistant plate is ideal for applications that require wear resistance but must be formable and weldable. Because of these properties, it can be used in a variety of different applications. It is particularly useful in applications where impact or sliding wear may be present.
Key Differences Between AR 400 and AR 500 Plates
Hardness:
AR 400 Steel: This grade has a nominal hardness of 400 Brinell (HB), which measures the hardness of a material. It is suitable for applications that require moderate to severe wear resistance, such as mining, construction, and material handling equipment.
AR 500 Steel: This grade has a higher nominal hardness of 500 Brinell, making it tougher and more wear-resistant than AR 400. It is often used in applications that require extreme wear resistance, such as target shooting, armored vehicles, and mining equipment.
Cracking:
AR 400 Steel: Compared to AR 500 steel, AR 400 is generally more ductile and ductile, meaning it is less prone to cracking, especially in applications involving high impact or dynamic loading conditions. However, it is important to consider that both grades of steel can still crack under extreme stress or improper use.
AR 500 Steel: This grade of steel is more susceptible to cracking when impacted than AR 400 steel, making it more suitable for use in sliding wear applications in agricultural, manufacturing, and mining machinery and equipment.
Applications:
AR 400 Steel: AR 400 wear resistance steel plate is often used in applications requiring moderate wear resistance and can be found in dump truck bodies, crushers, hoppers, and chutes.
AR 500 Steel: AR 500 abrasion resistant steel sheet is the preferred choice in applications requiring higher wear resistance and can be used in ballistic plates, shooting targets, and armor plates.
Machinability:
AR 400 Steel: AR 400 steel is generally considered easier to machine due to its lower hardness.
AR 500 Steel: This grade of steel can be machined, but it is more difficult to machine than lower grades. Appropriate cutting tools, techniques, and machining parameters are required to achieve satisfactory results.
Weldability:
AR 400 Steel: This grade of steel can be welded using proper procedures, but precautions need to be taken to avoid excessive heat input, which may affect the hardness and properties of the material.
AR 500 Steel: AR 500 Steel can be welded using proper welding procedures, but care must be taken to avoid excessive heat input, which may impair the hardness and properties of the material.
Typical Properties of AR 400 Abrasion Resistant Wear Plates
AR400 is a “through-hardened” wear-resistant alloy plate. Hardness range is 360/440 BHN, nominal hardness is 400 BHN. Service temperature is 400°F. This plate product is suitable for applications requiring a good balance of formability, weldability, toughness and wear resistance. Wear-resistant steels are usually sold by hardness range, not fixed chemical composition.
How to choose the cutting method of AR400 wear-resistant steel plate
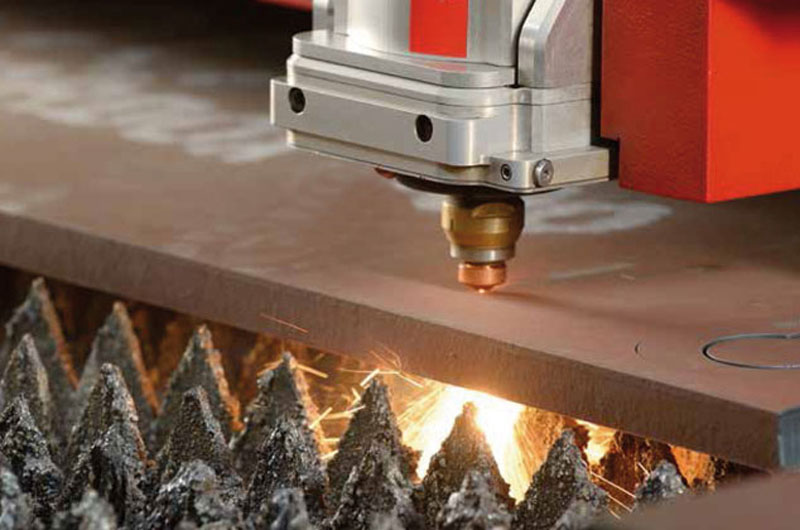
When cutting the plate, you need to pay attention to the hardness. The hardness of AR400 wear-resistant steel plate is related to the thickness. There are thin and thick AR400 wear-resistant steel plates on the market. Thick AR400 plates are harder and require more force when cutting. In order to prevent the influence of high temperature steel plate hardness, laser cutting or water jet cutting is generally selected when processing materials such as AR400 steel plates.
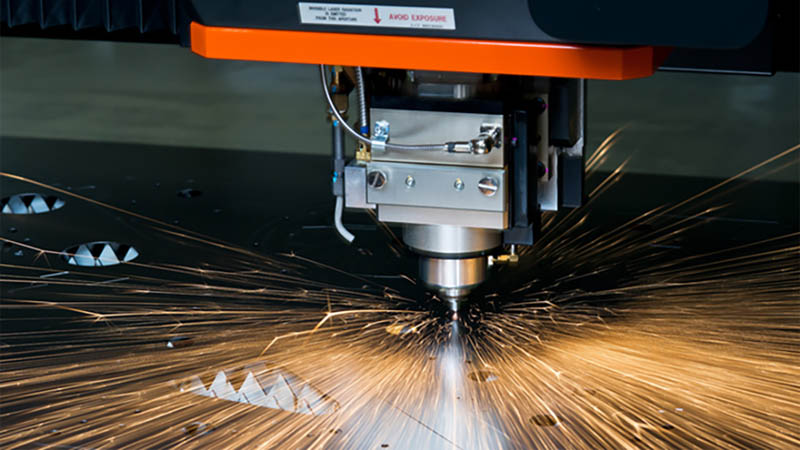

Laser cutting, as the name implies, uses the linear propagation characteristics of lasers and high-intensity energy to process steel plates. AR400 wear-resistant steel plates have high hardness. General flame cutting requires a lot of energy and time, and the effect of temperature on steel plates is irreversible. Laser cutting is fast and accurate, and is more suitable for this type of material.
Not to mention water jet cutting. Where there is water, the performance of AR400 wear-resistant steel plates can be guaranteed. However, due to the high cost of water jet cutting, it is still necessary to consider carefully when processing large quantities of plates. The processing of AR400 wear-resistant steel plates also includes bending, welding, etc. The steel plates need to be softened first to utilize their own toughness, and be careful not to crack due to excessive processing.